And Justice For All

ABOVE: “The Bostonians Paying the Excise Man.”
(1774 print, attributed to P. Dawe.)
Chastisement in the pursuit of justice remains one of the most hotly contested and debated issues of the day. From capital punishment to humiliation practices, consequences suffered by those who commit crimes are intended to set an example. The debate lies in how far one can go in the pursuit of righteousness. Many citizens today believe that more criminals deserve to be rehabilitated rather than incarcerated, while others rally for harsher and lengthier sentences. Recent accusations of torture and inhumane interrogation techniques have reopened the public’s examination of how prisoners should, and should not, be treated.
In the early days of primitive America, vigilante justice, or “mob rules,” commanded the streets as angry citizens took it upon themselves to act as judge, jury, and in some cases, executioner. Many of the methods used at this time were exceptionally painful and permanently scarring. Some of the harshest punishments can be traced back to the crown, hundreds of years before any Englishman ever set foot in the New World. Perhaps the most disturbing form of retribution to be dispensed in the colonial era was the act of tarring and feathering. This was an unsanctioned penalty in which an individual would have boiling hot tar poured over or brushed onto them, then they would be either covered in - or rolled in - feathers. Sometimes the person would be stripped naked and carried around town upon a rail. The goal was to humiliate them to the point that they would vacate the town, never to return.
This painful procedure was originally endorsed by English law in the late 1100’s. The earliest mention of “official” tar and feathering occurred in the orders of King Richard I of England, who issued them to his navy before sailing for the Holy Land in 1191. It is believed that this primitive ordinance aimed at criminal crusaders inspired the use of the technique in the colonies during the turbulent days leading up to the revolution. What follows is a transcript of what is believed to be the only royal declaration in existence that specifically instructs the use of tar and feathering:
Laws of Richard I (Coeur de Lion) Concerning Crusaders Who Were to Go by Sea. 1189 A.D. ("Roger of Hoveden," III p. 36 [Rolls Series].)
Richard by the grace of God king of England, and duke of Normandy and Aquitaine, and count of Anjou, to all his subjects who are about to go by sea to Jerusalem, greeting. know that we, by the common counsel of upright men, have made the laws here given. Whoever slays a man on ship. board shall be bound to the dead man and thrown into the sea. But if he shall slay him on land, he shall be bound to the dead man and buried in the earth. If any one, moreover, shall be convicted through lawful witnesses of having drawn a knife to strike another, or of having struck him so as to draw blood, he shall lose his hand. But if he shall strike him with his fist without drawing blood, he shall be dipped three times in the sea. But if any one shall taunt or insult a comrade or charge him with hatred of God: as many times as he shall have insulted him, so many ounces of silver shall he pay. A robber, moreover, convicted of theft, shall be shorn like a hired fighter, and boiling tar shall be poured over his head, and feathers from a cushion shall be shaken out over his head,-so that he may be publicly known; and at the first land where the ships put in he shall be cast on shore. Under my own witness at Chinon.
Source: Henderson, Ernest F.
Select Historical Documents of the Middle Ages
London: George Bell and Sons, 1896
What a weekend.
 This weekend I had a great time visiting with my friend Mort Kunstler (View a PDF of my FLS article) and speaking at the VA Farm Bureau Women’s Conference on the life and legacy of Mary Ball Washington. It was clearly the largest room that I have done to date (300+ attendees) and I will be receiving a copy of the video that was recorded for broadcast to post here. The feedback that I received on this particular piece was extremely encouraging. As a result, I will be submitting a more scholarly and in-depth version to Patriots of the American Revolution for inclusion in an upcoming issue. Stay tuned for the VAFB video which will be posted upon receipt. I would like to add that Virginia's farmers deserve our thanks and support. If you like to eat, remember where it comes from.
This weekend I had a great time visiting with my friend Mort Kunstler (View a PDF of my FLS article) and speaking at the VA Farm Bureau Women’s Conference on the life and legacy of Mary Ball Washington. It was clearly the largest room that I have done to date (300+ attendees) and I will be receiving a copy of the video that was recorded for broadcast to post here. The feedback that I received on this particular piece was extremely encouraging. As a result, I will be submitting a more scholarly and in-depth version to Patriots of the American Revolution for inclusion in an upcoming issue. Stay tuned for the VAFB video which will be posted upon receipt. I would like to add that Virginia's farmers deserve our thanks and support. If you like to eat, remember where it comes from.
Via email: I thoroughly enjoyed your presentation and perspective on Mary Ball Washington. That was the fastest half hour of history I have attended! For me, you could have gone on the rest of the morning.
Doug Stoughton
Director, Women and Young Farmer Department
Virginia Farm Bureau Federation
May I take your coat sir?
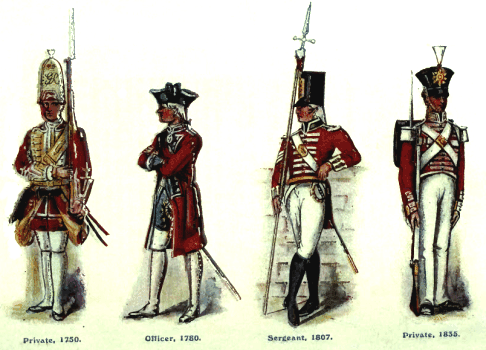
ABOVE: British Army infantry uniforms from 1750 to 1835.
Source: Regimental Nicknames and Traditions of the British Army. (London: Gale & Polden. 1916.)
Today I thought I would share something a little more casual and just for fun… My father has a tremendous collection of records which include a complete set of Bill Cosby’s comedy albums. A good part of my childhood memories include scenes of the family, sitting around the old stereo, listening to some of the funniest bits ever captured on vinyl. One of my favorites is a record titled “Bill Cosby is a Very Funny Fellow Right?” (or something like that). There is a routine from that performance in which Cosby pitches the concept of a referee holding a coin toss at the beginning of a war. He uses the American Revolution as the basis, and after making the right call, the Continentals choose to ‘kick off,’ and add that “We can wear whatever color uniforms we like, and hide behind trees and rocks and stuff, and you British have to wear bright red, and march out in the open in a straight line.” That punch-line stuck with me and even to this day, every time I see a depiction of a Redcoat, that joke enters my mind. What makes it so funny is that it’s true.
Clearly the Brits had far better tailors than the Continentals, but form over function has never worked on the battlefield. In their quest to look their best, many of the King’s finest suffered death by wardrobe. We know this as there have been studies by military historians that cite the affect of heavy and cumbersome uniforms on the army. They have determined that the regulation style uniforms worn by the English troops contributed to needless suffering en route to defeat. There was even an episode of “Battlefield Detectives” on the History Channel in which they concluded that a group of British soldiers who were cut off from any shade or water supplies were beaten by a much smaller force of militia, who pinned them in and simply prevented them from moving (in a siege like state). As the hours passed their enemy fell into a deadly state of heat exhaustion and dehydration. The investigators even went so far as to put two modern-day British Commandos on treadmills, one in the sparse attire worn by the minutemen and the other in a traditional garb worn by English infantry. The Continental fared well, while the Redcoat almost passed out. (Of course the opposite was true in the winter-months and the rebels lightweight gear left much to be desired at places like Valley Forge.)
According to excerpts cited from "History of the Regiments & Uniforms of the British Army" by Maj. R.M. Barnes, “The red coat has evolved from being the British infantryman's ordinary uniform to a garment retained only for ceremonial purposes. Its official adoption dates from February 1645, when the Parliament of England passed the New Model Army ordinance. The new English Army (there was no 'Britain' until the union with Scotland in 1707) was formed of 22,000 men, divided into 12 foot regiments of 1200 men each, 11 horse regiments of 600 men each, one dragoon regiment of 1000 men, and the artillery, consisting of 50 guns. In the United States, "Redcoat" is associated with British soldiers who fought against the colonists during the American Revolution. It does not appear to have been a contemporary expression - accounts of the time usually refer to "Regulars" or "the King's men". Abusive nicknames included "bloody backs" (in a reference to both the colour of their coats and the use of flogging as a means of punishment for military offences) and "lobsters" (most notably in Boston around the time of the Boston Massacre). It is not until the 1880s that the term "redcoat" as a common vernacular expression for the British soldier appears in literary sources, such as Kipling's poem "Tommy", indicating some degree of popular usage in Britain itself. However an isolated earlier use of this term relating to the American War of Independence appears in "The Riflemen's Song at Bennington", an old folk song that supposedly [citation needed] goes back to the 1770s.”
Someone once said that it is “better to look good than to feel good.” Another remarked that you should “always dress for success.” I wonder if the former was an officer in the English Army.
PS. This weekend I’ll be spending Saturday with Mort Kunstler at his Fredericksburg print signing and Sunday I’ll be giving my speech on Mary Ball Washington at the VAFB Women’s Convention. Hopefully I’ll have photos and a video to share next week.
2010 Event Schedule
I am periodically available for speaking engagements, book signings, radio shows, documentary/television appearances and online chat presentations. Fees and travel expenses are negotiable. Power Point projection requested for speaking events. I will provide the media. *Discounts and/or fees waived for church, military and non-profit groups. Please note that I will only write NEW topics on the Colonial-period. I can present past Civil War talks. See transcripts below. Email for booking info.
March 21, 2010 VA Farm Bureau Women's Conference: Mary Ball Washington, The Mother of the Father of Our Country (Fredericksburg Hospitality House)
June 5, 2010 Book Signing: "Gathering of Eagles" (Winchester Courthouse Museum)
Will return to in 2011.
June 19, 2010 CWHC Muster Banquet: "Jackson's Journey, Stonewall in the Valley" (Lexington Holiday Inn Express)
July 24, 2010 Premiere party: "The Angel of Marye's Heights" documentary.
(Central Rappahannok Regional Library)
September 18, 2010 Screening: "The Angel of Marye's Heights" documentary. (Liberty University Campus)
October 9, 2010 Civil War Author's Book Signing: "Germannafest," Germanna Community College 40th Anniversary Celebration (Locust Grove)
October 21, 2010 "Mary Ball Washington, The Mother of the Father of Our Country" (Stafford County Courthouse Administration Center)
November 13, 2010 Book Signing and Vignettes: "Civil War Author's Day" (Gray Ghost Vineyards and Winery)
Date(s) TBD "The Angel of Marye's Heights" film opening and screenings.
Date TBD NCWLF "Campfires at the Crossroads: Letter Readings" (CW Life Museum)
PAST TRANSCRIPTS:
Richard Kirkland "The Angel of Marye's Heights"
Race Relations at Fredericksburg's Landmark Churches
Backyard History: Lee's Hill Community
Houses of the Holy: Fredericksburg's Churches
The Great Revival in the American Civil War
Faith under Fire: Discipleship during the Civil War
Christ in the Camp by Rev. J. William Jones
Effective Historic Research and Writing
Radio Shows, Chatroom Discussions, and Misc. Events
Commercial and Documentary Appearance samples
Inaugural Guest Post
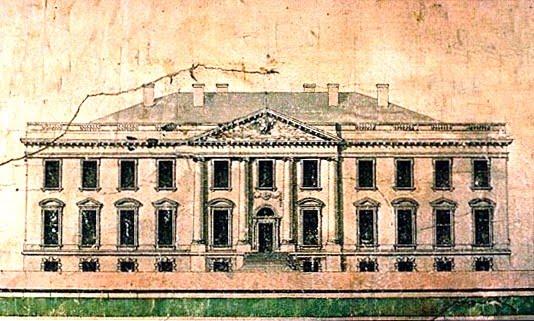
ABOVE: c 1793 Elevation of the original White House, by James Hoban. (MD Historical Society)
One of the new additions to “Blog, or Die.” will be periodic guest posts by fellow historians. Our first candidate and I have collaborated for years over at The Jefferson Project and The Free Lance-Star Town & County. His name is Chris Williams and he is a graduate of VCU, very active politically in the African-American community, and a contributing writer to such award-winning publications as Street Report Magazine. Chris is also an R&B songwriter and producer. His specialty is correlating early American history to today and he has penned several outstanding pieces on Black History Month.
Chris and I have a sincere respect for one another and we often have difficult discussions over issues like racism and historical memory. It was his interpretations of the Founding Fathers that initiated the TJ Project. We don’t always agree, but we glean wisdom from each other’s views and our work is far better for it. Chris recently suggested that we construct some pieces regarding race from the Old America to the New America and in a recent email to me he wrote, “Race is a topic that is almost a societal taboo to speak on, but I have no problem expressing my opinions on it because it's something that we all deal with every day in different ways.”
I asked my friend if he would allow me to share a piece he penned on the origins of the White House. In it he brilliantly integrates the history of the building with the historic presidency that dominated the attention of the day. This article ran just before President Obama’s inauguration and is incredibly fascinating. As the issue of race has become a regular topic here, I can’t think of a better way to kick-off our guest posts than sharing this seldom discussed piece of American history.
THE WHITE HOUSE AND OBAMA
By Chris Williams
FLS (T&C), January 17, 2009
Since its inception, the White House has been a representation of liberty, democracy and independence. What many Americans don't know is how the actual building was constructed and the correlation it has with the heritage of our incoming president, Barack Obama, whose inauguration is Tuesday.
Obama's heritage has intrigued both Republicans and Democrats, but in researching the history of the White House I found striking similarities between the ancestral lineages of the people who designed and built it and of the man who will be residing there next week.
As the story goes, in 1790 the first U.S. Congress approved the Act of Residence to create the permanent seat of the federal government. The act empowered President George Washington to locate America's capital along the Potomac and Anacostia rivers.
It designated Philadelphia as the temporary capital for 10 years until the completion of a presidential residence and a capitol in Washington.
George Washington had a grand vision for the buildings. They would be emblematic of the democracy that America acquired just nine years earlier with the surrender of British troops in the Revolutionary War.
Pierre Charles L'Enfant and Benjamin Banneker devised the original plans for the city of Washington, but those plans were held in abeyance until an architect was found.
Secretary of State Thomas Jefferson proposed that a national design competition be held to determine the designer of the president's house and Congress' house--the "capitol," the term Virginians used for their statehouse.
The winner of this competition was an Irish architect named James Hoban. Through happenstance, he had met George Washington a year earlier in Charleston, S.C., when Washington was visiting personal friends. Little did they know that a year later they would be joining forces to bring Washington's vision to fruition.
The buildings Hoban designed directly reflected the 18th-century Georgian neoclassical style of the house of the Duke of Leinster in Dublin, Ireland. These designs stood out to Washington because he was fascinated by edifices located in Europe.
"In the last part of the eighteenth century, Americans and the Irish had the same political convictions along with shared strategies in economic development for their countries," according to William Seale, author of "The White House: An American Idea."
It is not known whether this played a role in Washington's choice of Hoban, but his plans were approved in the autumn of 1792 with changes forthcoming a year later.
To proceed with the implementation, the U.S. government planned to import workers from Europe, but recruitment yielded abysmal results. The government then sent out a request for 100 slaves to begin the arduous task of constructing the White House.
The laying of the cornerstone took place on Oct. 13, 1792.
There was a Fredericksburg-area connection to the original construction of the White House. In 1793, enslaved and free blacks from Virginia and Maryland began clearing the forest for the White House and Capitol, digging trenches and ditches and bringing sandstone piece by piece on boats from the Aquia Creek quarry in Stafford County.
They also began hauling lumber and other materials from White Oak Swamp in what is now King and Queen County, and placing cut stones for the walls of the White House.
According to Seale, "City commissioners of the project were concerned that this local source of sandstone couldn't provide the sufficient quantity necessary to produce the White House and the Capitol so they decided to downscale the size of the White House to keep the plans intact. Due to the reduction in size, the White House now in a sense was 'Americanized' because of the loss of the most obvious reference to the Leinster House, which was the high base, but Washington demanded to keep the ground dimensions of the enlarged plans."
Brickmasons worked hand in hand with the stone-masons to provide stability for the structure of the White House.
"The credit for carving the stone for the first White House belonged to two groups of Scottish immigrants who were stonemasons that faced a moratorium from the building industry in England due to the war with revolutionary France," according to Seale.
These two groups of immigrants consisted of members of the Masonic order in Washington and two brothers, John and James Williamson (who were not related to the chief stonemason, Collen Williamson, also from Scotland).
By 1795, Williamson and Hoban no longer saw eye to eye and Williamson was replaced by an English mason, George Blagdin. But it was another Englishman, Benjamin Henry Latrobe, along with Thomas Jefferson, Dr. William Thornton and James Hoban, who saw through the completion of the original White House and Capitol.
Once the construction was finished, the porous sandstone walls were coated with a mixture of lime, rice glue, casein and lead, giving the house its familiar color and name. The first president to inhabit the residence was John Adams in 1800.
Hoban and Latrobe were also responsible for overseeing the reconstruction of the White House after it was burned by the British during the war of 1812.
OBAMA CONNECTION
In this research, I came across some surprising similarities between the lineage of James Hoban and that of President-elect Barack Obama.
Hoban's lineage traces back to the province of Leinster; Obama's great-great-great-grandfather on his mother's side, Falmouth Kearney, also was from the province of Leinster.
Hoban was from County Kilkenny, and Falmouth Kearney was from nearby County Offaly.
It has been well documented that Obama is a distant cousin of President Harry Truman, Vice President Dick Cheney and former British Prime Minister Winston Churchill through their common ancestor, Mareen Duvall.
Obama's English and Scotch-Irish roots can be traced back to the 1650s to Duvall, a wealthy Huguenot merchant who immigrated to Maryland during the mid-17th century.
The fact that Obama's father was African brings into the equation the role of African-Americans in constructing the White House. Their work alongside the Scotch-Irish immigrants was pivotal in laying the foundation and molding the designs for what was variously called the President's Palace, the Presidential Mansion, the President's House, the Executive Mansion and, as it was to be named later by Theodore Roosevelt, the White House.
Each of these disparate groups contributed to crafting a building that will be home to one of its own after the swearing-in of our 44th president on Tuesday night.
President-elect Obama's African, English and Scotch-Irish background make him an anomaly in the sphere of American politics. His election will go down in the time-honored annals of the White House.







 This weekend I had a great time visiting with my friend Mort Kunstler (
This weekend I had a great time visiting with my friend Mort Kunstler (